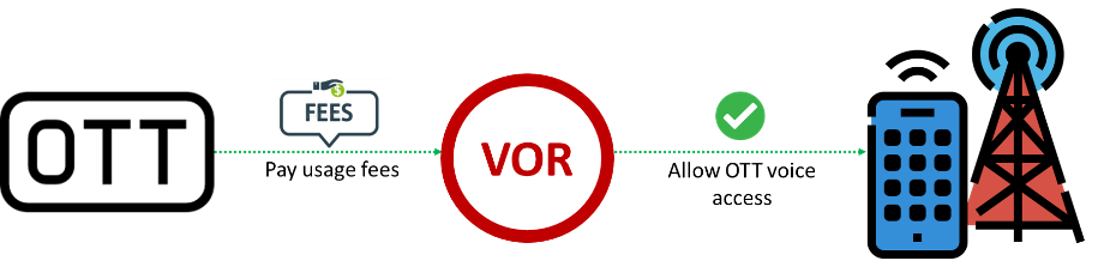
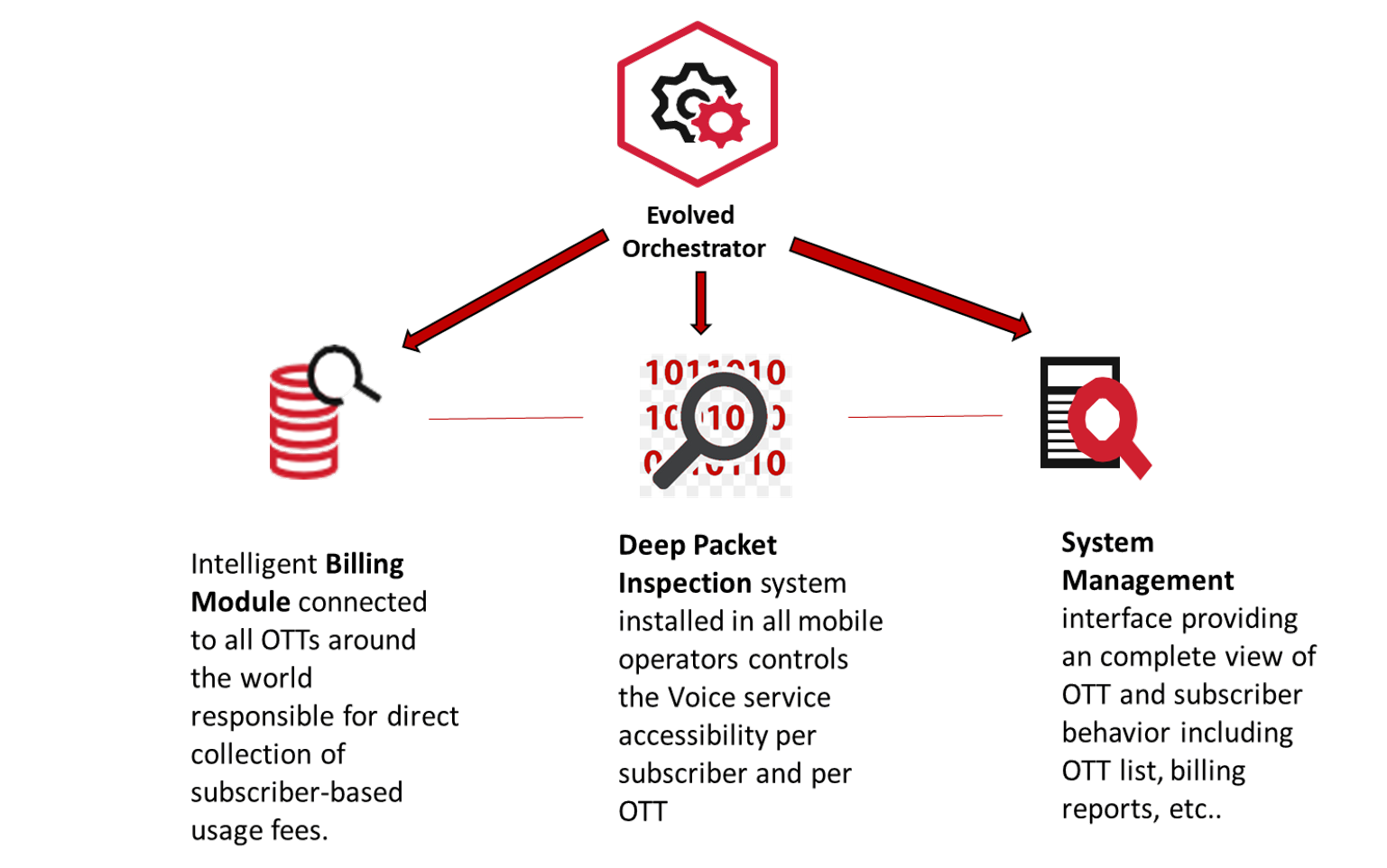
VOR
MONETIZING "OVER THE TOP SERVICES" WITHOUT IMPOSING EXTRA CHARGES ON THE END USERS
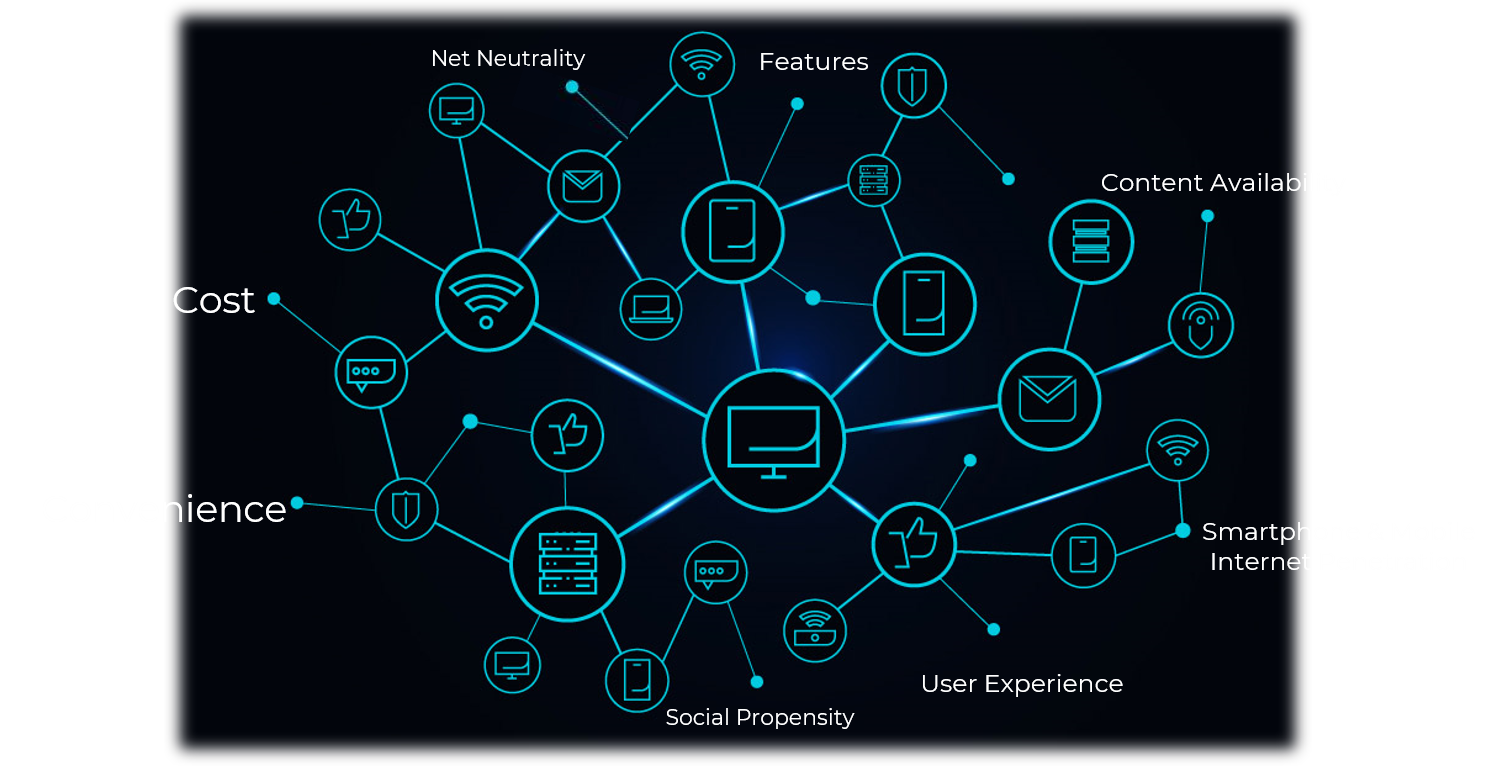
WHAT ARE THE
OTTS?

“No legal definition”

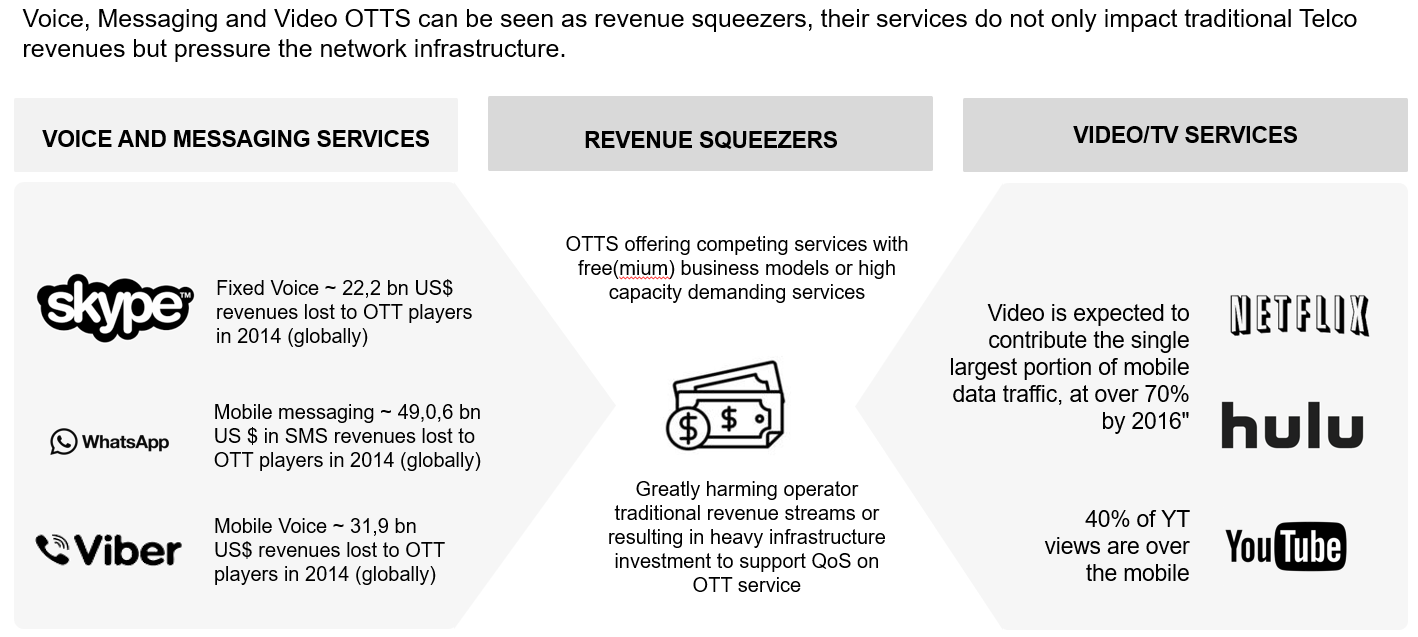
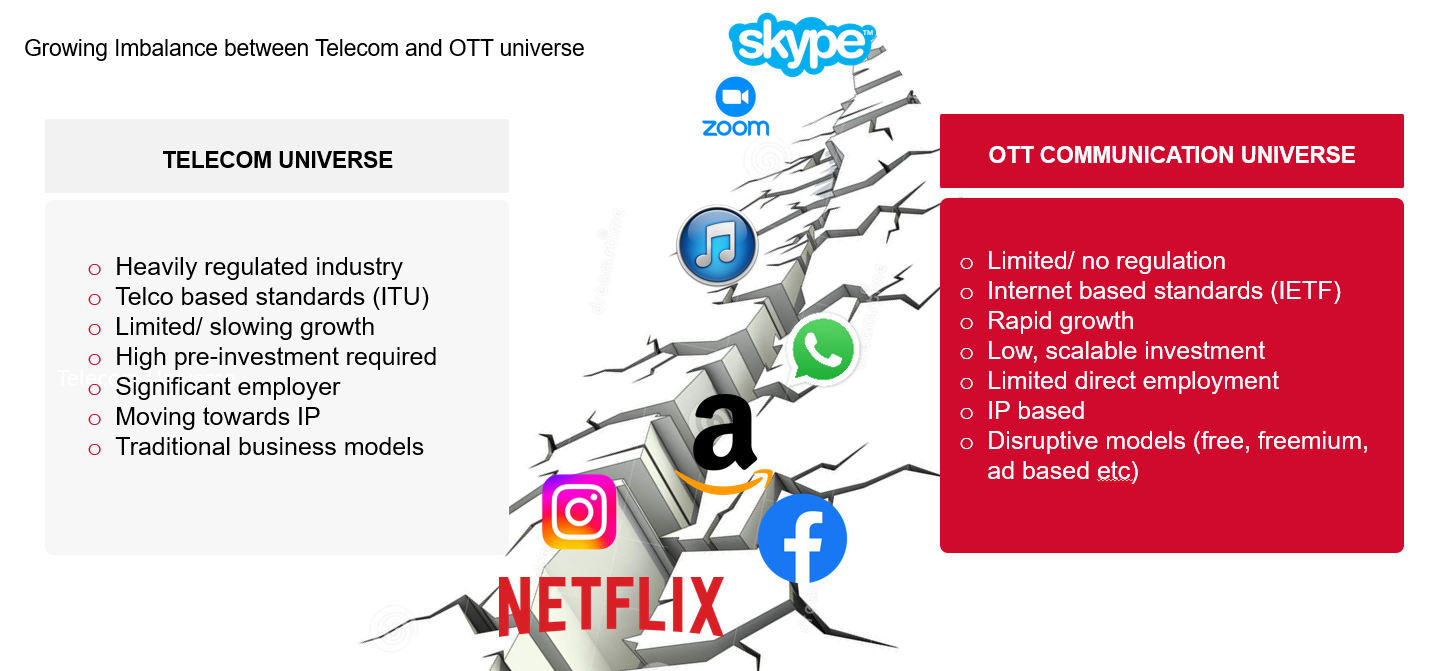
LEADING TO OTT
EVOLUTION AND GROWTH